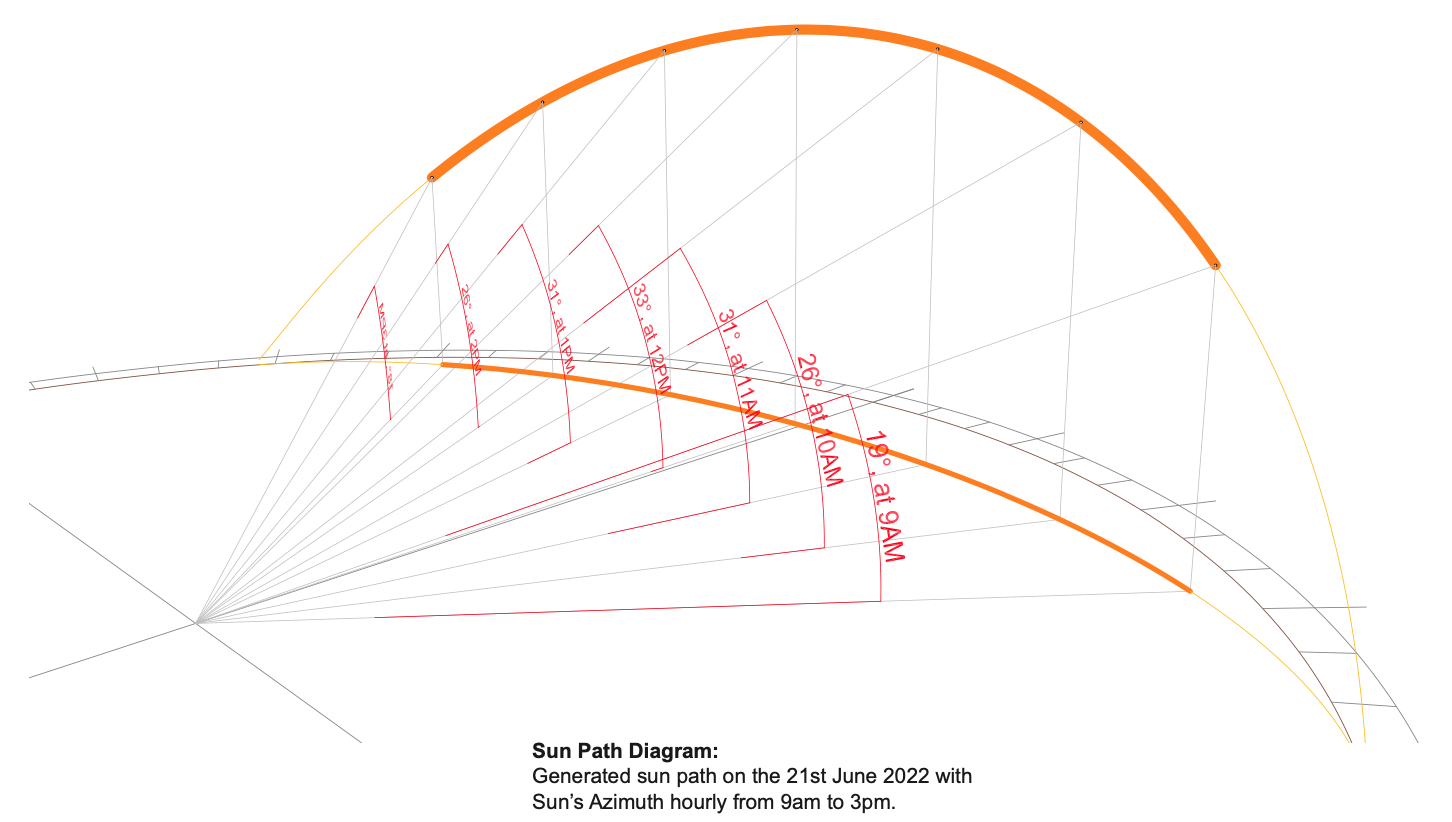
How are Sun Eye Diagrams conducted?
Sun eye diagrams are produced using accurate 3D modelling and solar analysis software that simulates the path of the sun based on real-world astronomical and location data. A three-dimensional model of the proposed building is created and positioned within its true geographic context, allowing the sun’s movement to be analysed in relation to the building form and its surroundings across different times of day and seasons of the year.
The analysis incorporates key site-specific information such as the building’s orientation, height, massing, setbacks, surrounding structures, and local latitude. This ensures that the resulting sun and shadow projections accurately reflect how the development will perform within its actual environment. By testing critical dates and times—such as solstices, equinoxes, and peak sunlight hours—the sun eye diagram provides a comprehensive understanding of overshadowing and solar access impacts.
In developing a meaningful outcome for each project, design intent and usage are also considered. This includes identifying sensitive areas such as neighbouring windows, private open spaces, balconies, and public realms where access to sunlight is important. The 3D sun eye model allows these elements to be viewed dynamically, offering a clear and intuitive understanding of how shadows move and interact with the built form.
Once the analysis is complete, high-quality images and visual outputs are generated directly from the 3D model. These can be used to inform design refinements—such as adjusting building height, massing, orientation, or setbacks—to improve solar performance and reduce overshadowing where required. The same images can also be submitted as supplementary material to council.
Through this process, sun eye diagrams provide a robust and transparent method for evaluating solar impacts, helping clients achieve better design outcomes while reducing planning risk and approval uncertainty.